InfiniBench: Infinite Benchmarking for Visual Spatial Reasoning with Customizable Scene Complexity
Abstract
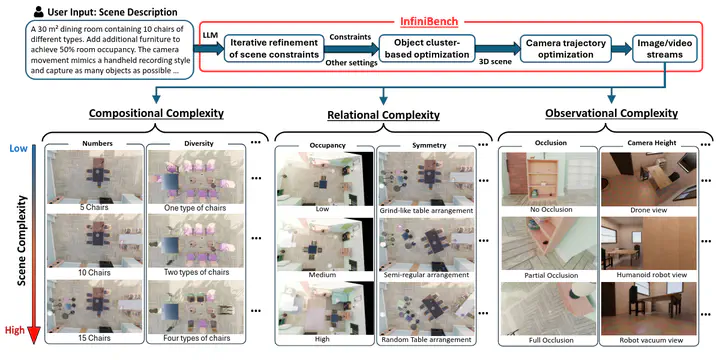
Modern vision-language models (VLMs) are expected to have abilities of spatial reasoning with diverse scene complexities, but evaluating such abilities is difficult due to the lack of benchmarks that are not only diverse and scalable but also fully customizable. Existing benchmarks offer limited customizability over the scene complexity and are incapable of isolating and analyzing specific VLM failure modes under distinct spatial conditions. To address this gap, instead of individually presenting benchmarks for different scene complexities, in this paper we present InfiniBench, a fully automated, customizable and user-friendly benchmark generator that can synthesize a theoretically infinite variety of 3D scenes with parameterized control on scene complexity. InfiniBench uniquely translates scene descriptions in natural language into photo-realistic videos with complex and physically plausible 3D layouts. This is achieved through three key innovations. 1) a LLM-based agentic framework that iteratively refines procedural scene constraints from scene descriptions; 2) a flexible cluster-based layout optimizer that generates dense and cluttered scenes previously intractable for procedural methods; and 3) a task-aware camera trajectory optimization method that renders scenes into videos with full object coverage as VLM input. Experiments demonstrate that InfiniBench outperforms state-of-the-art procedural and LLM-based 3D generation methods in prompt fidelity and physical plausibility, especially in high-complexity scenarios. We further showcased the usefulness of InfiniBench, by generating benchmarks for representative spatial reasoning tasks including measurement, perspective-taking and spatiotemporal tracking.
Agentic Generation of Scene Constraints
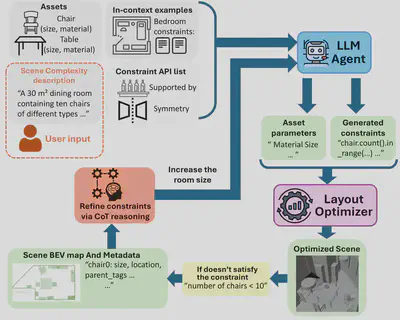
InfiniBench iteratively refines the generated scene constraints via a critical feedback loop. In each iteration, we use the scene layout optimizer described to attempt realizing the generated constraints into a 3D scene. If the optimizer fails, the returned error report, which includes a bird’s eye view (BEV) map showing object collisions and a textual summary describing the unmet constraints, is fed back to the LLM agent to refine the constraint generation. Such refinement enforces a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning process that prompts the LLM agent to first analyze the failure, propose a solution accordingly, and then implement the changes on scene constraints.
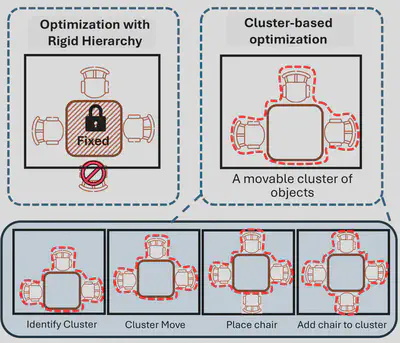
Layout Optimization for Complex Scenes
To ensure robust layout optimization with high scene complexity, we restructured the layout engine with a flexible cluster-based optimization strategy. This strategy, builds on a new concept of movable cluster, defined as a dynamic group of related objects (e.g., a table and chairs surrounding it) that are treated as a single entity in optimization.
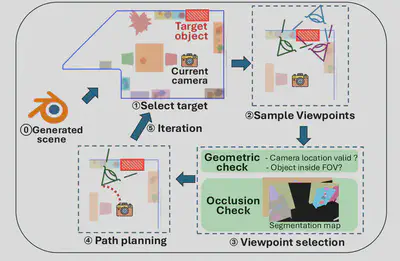
Camera Trajectory Optimization
Our method is inspired by frontier-based exploration, a classical robotic navigation technique. Unlike traditional approaches that explore frontiers using occupancy grids, we define ``frontiers’’ as the set of unvisited target objects. We then develop a viewpoint sampling method to find optimal views for these targets while avoiding occlusion.
Associated Dataset
We also published the associated dataset together with this paper.
