Modality Plug-and-Play: Runtime Modality Adaptation in LLM-Driven Autonomous Mobile Systems

Abstract
Multimodal reasoning by LLMs is critical to autonomous mobile systems, but the growing diversity of input data modalities prevents incorporating all modalities into LLMs. Instead, only the useful modalities should be adaptively involved at runtime, based on the current environmental contexts and task requirements. Existing work on runtime modality adaptation uses fixed connections between data encoder and LLM’s input layer, but results in high training costs and ineffective cross-modal interaction. In this paper, we present MPnP, a new modality adaptation technique that connects data encoders to a flexible set of last LLM blocks and makes such latent connections fully trainable at runtime. Evaluation results show that MPnP has high compute and data efficiency, with 3.7× FLOPs reduction and 30% memory usage reduction compared to best baselines. It requires only few hundreds of training samples at runtime, and completes modality adaptation within few minutes on weak devices.
The Need of Efficient Runtime Modality Adaptation
Large Language Models (LLMs) can do reasoning over diverse input data modalities besides the natural language domain. One major challenge of such multimodal reasoning is the growing diversity of input data modalities and limited performance of resource-constrained edge devices. A good solution is to adaptively involve only the useful modalities at runtime for the minimum on-device computing cost, such as the runtime modality adaptation for multimodal QA in autonomous driving example as shown in the image above.
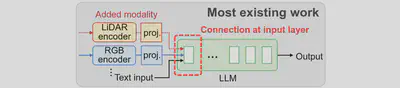
Jointly train the encoders of all involved modalities with LLM to align every modality with the natural language domain, but is too expensive for runtime. As shown below, Most existing work only fine-tune the trainable projector that connects modal encoder to LLM’s input layer, but still require backpropagating throughout the entire LLM with high training costs.
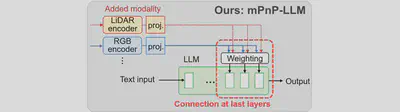
mPnP-LLM Design
As shown in the image below, we present Modality Plug-and-Play in multimodal LLMs (mPnP-LLM), a new technique for elastic, automated and prompt runtime modality adaptation in multimodal LLMs, by connecting unimodal encoders to a flexible set of last LLM blocks and making such latent connections fully trainable at runtime. We can adaptively adjust the amount of LLM blocks being connected for different tradeoffs between accuracy and runtime training cost. We can also optimize the efficiency of cross-modal interaction and hence improve accuracy, by controlling the amount of information being injected in each connection with a trainable weighting module.
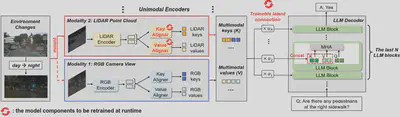
In our design, mPnP-LLM adapts new input modalities and connects the corre- sponding unimodal encoders to LLM blocks via the (1) Key & Value Aligners module, and (2) Trainable Latent Connection module. An example for the multimodal QA task between two input modalities, namely RGB camera view and LiDAR point cloud, is shown in the figure below.
Experimental Results
We use the nuScenes-QA dataset for multimodal visual QA in autonomous driving, with results from workstation-level desktop platforms with RTX A6000 and mobile platform of Nvidia Jetson AGX Orin. Our processed dataset is published as the NuScenes-QA-mini dataset.
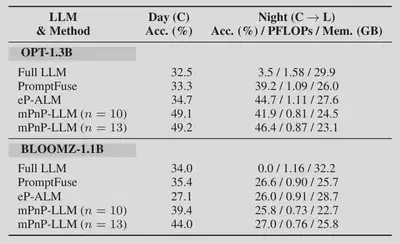
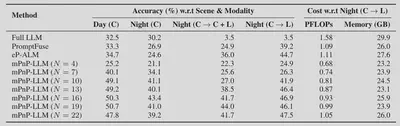
Compared with existing approaches, mPnP-LLM achieves better accuracy under similar costs.
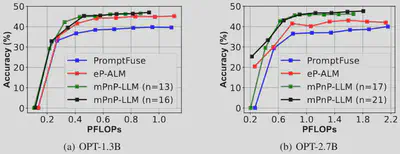
Under the same setup of night condition with LiDAR modality mounted on top of RGB modality, mPnP-LLM achieves better accuracy-compute tradeoff.
With different LLMs, mPnP-LLM ahieves higher accuracy than baseline schemes, and reduces the training FLOPs by 20%-37% and GPU memory consumption by up to 30%.